C++로 Stack 만들기 version 3.1
LinkedList 방식으로 작동하는 Stack을 만들어 보겠다.
Node끼리의 연결 방식으로 만들어 줌으로써 배열의 문제점인 크기 고정, 삽입 / 삭제의 제약을 해결하고 기억장소를 보다 효율적으로 사용할 수 있다.
LinkedList와 ArrayList의 큰 차이점으로는 삽입/삭제시 LinkedList가 ArrayList보다 빠르다는 것과 traverse시에는 ArrayList가 LinkedList보다 빠르다는 점이 있다.
이번 스택은 LinkedList로 단순하게 구현 → Garbage collector 기능 추가 → Information hiding 신경 써서 구현의 세 가지 버전으로 나눠서 만들어 볼 것이다.
Node라는 클래스를 만들어 데이터들을 다루는 객체로써 활용하는 스택을 만들어 보겠다.
먼저 메인함수이다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Stack.h"
void main()
{
/*Stack a;
Stack b;
Stack c;
a.push(10);
a.push(20);
a.push(30);
int x = a.pop();
a.push(40);
printf("%d\n", x);
printf("%d\n", a.pop());*/
Stack *a;
a = new Stack();
//Stack *b = a;
a->push(10);
a->push(20);
a->push(30);
int x = a->pop();
a->push(40);
for (int i = 100; i < 120; i++) {
a->push(i);
}
printf("%d\n", x);
printf("%d\n", a->pop());
a->print();
delete a;
//delete b;
}Stack 객체를 생성하여 push()와 pop(), print()의 작업을 해볼 것이다.
스택 사용 방법은 어느 자료구조로 구현하든 다름이 없다.
Stack의 헤더 파일을 보겠다
#include <stdio.h>
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
class Stack {
Node *top;
void stackEmptyError();
public:
Stack();
~Stack();
void push(int x);
int pop();
int peek();
void print();
};Linked List로써 사용할 이번 Stack은 노드 단위로 데이터를 저장할 것이기 때문에 Node 클래스를 만들어준다.
Stack의 Data member로는 top의 위치를 가리킬 Node 레퍼런스만 있으면 될 것이다. Node는 값을 보관할 변수 data와 그 다음 노드를 가리킬 next 레퍼런스를 데이터 멤버로써 가진다.
그림으로 간단히 보자면
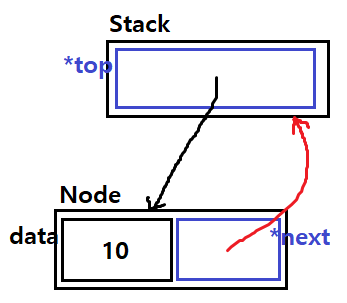
push()로 값을 넣을 때마다 Node가 생성 및 연결된다. 그리고 생성된 노드의 next는 항상 top을 가리키게 하고 push된 현재 노드를 top으로 지정한다.
push()는 아래 그림처럼 진행될 것이다.
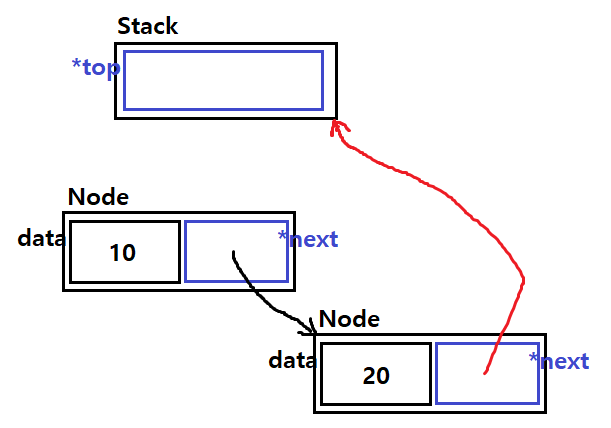
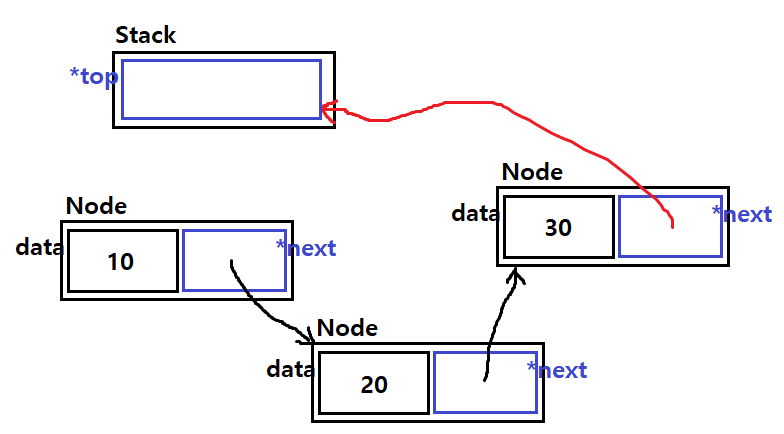
이런 식으로 push 작업이 이뤄지도록 하면 될 것이다.
pop()은 스택이 비어있을 경우(top이 NULL인 경우)는 예외 처리해주고, 데이터가 있을 때 리턴 할 변수를 top->data로 보관하고 top의 위치를 다음 노드로 바꿔준다.
peek()는 top의 data만 가져와서 리턴해준다.
print() 함수는 top을 가리키는 포인터 노드 tmp를 선언하여 tmp가 NULL이 아닌 동안 traverse 시킨다.
tmp의 data값을 출력시켜주고 tmp = tmp->next를 해주며 다음 데이터가 남아있는 동안 출력시킨다.
#include "Stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
Stack::Stack()
{
top = NULL;
}
Stack::~Stack()
{
}
void Stack::print()
{
printf("[");
Node *tmp = top;
while (tmp != NULL) {
printf("%d", tmp->data);
if (tmp->next != NULL) {
printf(",");
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
printf("]\n");
}
void Stack::push(int x)
{
Node *tmp = new Node(x);
tmp->next = top;
top = tmp;
}
int Stack::pop()
{
if (top == NULL) stackEmptyError();
int x = top->data;
top = top->next;
return x;
}
int Stack::peek()
{
if (top == NULL) stackEmptyError();
return top->data;
}
void Stack::stackEmptyError()
{
printf("Stack Empty!!!\n");
exit(-1);
}
version 3.2로 내용 보완을 해보겠다.
'Data Structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C++ Stack 만들기 (version.3.2 - LinkedList Stack) (0) | 2023.03.18 |
|---|---|
| C++ Queue 만들기 (version.4 - LinkedList Queue) (0) | 2023.03.18 |
| C++ Queue 만들기 (version.3 - Growable Array Queue) (0) | 2023.03.16 |
| C++ Stack 만들기 (version.2 - GrowableArray Stack) (0) | 2023.03.15 |
| C Circular Queue 만들기 (0) | 2023.03.14 |




댓글